0. 개요
현재 프로젝트에서는 마케팅팀이 넘겨주신 csv 파일을 파싱해서 DB 에 저장하는 로직을 가지고 있었다.
@Transactional(rollbackOn = RuntimeException.class)
public void read() throws RuntimeException {
try (InputStream inputStream = new ClassPathResource("data.csv").getInputStream();
CSVReader csvReader = new CSVReader(new InputStreamReader(inputStream))) {
List<DataRow> dataList = csvReader.readAll().stream()
.map(DataRow::of)
.toList();
for (DataRow row : dataList) {
// item table 저장된것 조회
int price;
int minAge;
int maxAge;
try {
price = Integer.parseInt(row.getPrice());
} catch (NumberFormatException e) {
price = 0;
}
try {
minAge = Integer.parseInt(row.getMinAge());
} catch (NumberFormatException e) {
minAge = 0;
}
try {
maxAge = Integer.parseInt(row.getMaxAge());
} catch (NumberFormatException e) {
maxAge = 100;
}
Item item = itemRepository.save(
Item.builder()
.id(row.getId())
.name(row.getItem())
.brand(row.getBrand())
.description(row.getDescription())
.price(price)
.minAge(minAge)
.maxAge(maxAge)
.build()
);
// category 있는지 조회 후 없으면 저장
Category category = categoryRepository.findByName(row.getCategory())
.orElseGet(() -> categoryRepository.save(
Category.builder()
.name(row.getCategory())
.build()
));
// 이미 매핑된 item_category의 경우 제외하고 저장
if (!itemCategoryRepository.existsByItemAndCategory(item, category)) {
itemCategoryRepository.save(
ItemCategory.builder()
.item(item)
.category(category)
.build()
);
}
...
JPA 를 사용하여 데이터를 처리해서 table 당 데이터들을 개별적으로 처리하는 구조로 되어 있다.
save 메서드를 호출할 때마다 영속성 컨텍스트가 flush 를 호출하여 DB 에 반영하고, commit 할 때마다 트랜잭션이 커밋되며 매번 DB 에 대한 쿼리가 발생한다.
이렇게 데이터를 insert 해주니 1000건 데이터 관련 거의 30분 가량의 오랜 시간이 소요되어서
Batch Insert 를 적용해서 DB 에 대한 요청 횟수를 줄여보는게 좋겠다는 생각이 들었다.
1. JPA vs JDBC Batch Insert
고민이 되었던 점은 Jpa 와 JDBC Batch Insert 중 무얼 사용하는게 맞을까 ? 였다.
현재 Data Parser 로직은 연관관계로 묶인 여러 테이블들이 join 되어 있었고 이에 해당하는 data row 하나하나 insert 해줬어야 했다.
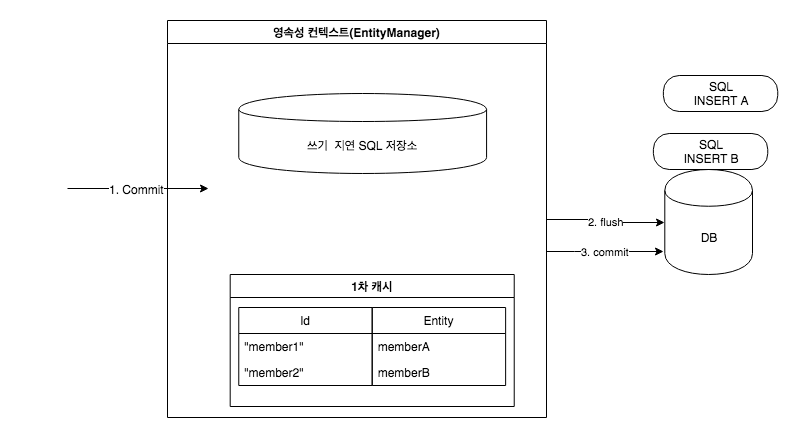
JPA 는 위의 그림과 같이 영속성 컨텍스트(EntityManager) 관리와 flush 및 쿼리 생성하는 추가적인 작업이 있고,
JDBC는 단순히 SQL 명령어를 실행하는 데 초점이 맞춰져 있어서 성능이 훨씬 빠를 것 같았다.
물론 JPA는 @OneToMany, @ManyToOne 등 관계를 자동으로 관리해 주기 때문에 복잡한 SQL을 작성할 필요가 없다는 장점도 있다.
@Transactional
public void parseAndInsertData(List<DataRow> dataRows) {
try {
String insertSql = "INSERT INTO item (id, name, brand, price, description) VALUES (?, ?, ?, ?, ?)";
String categorySql = "INSERT INTO category (name) VALUES (?) " + "ON CONFLICT (id) DO UPDATE SET name = EXCLUDED.name";
String itemCategorySql = "INSERT INTO category (name) VALUES (?)";
String itemUrlSql = "INSERT INTO item_url (item_id, url) VALUES (?, ?)";
String itemJobSql = "INSERT INTO item_job (item_id, name, step) VALUES (?, ?, ?)";
String filterSql = "INSERT INTO item_filter (item_id, filter_id, name) VALUES (?, ?, ?)";
List<Object[]> itemBatchArgs;
List<Object[]> categoryBatchArgs;
List<Object[]> itemCategoryBatchArgs;
List<Object[]> itemUrlBatchArgs;
List<Object[]> itemJobBatchArgs = new ArrayList<>();
List<Object[]> filterBatchArgs = new ArrayList<>();
long situationId = 2L;
long emotionId = 3L;
long genderId = 4L;
long preferenceId = 5L;
long typeId = 6L;
long relationId = 7L;
itemBatchArgs = dataRows.stream()
.map(row -> {
int price = 0;
if (row.getPrice() != null && !row.getPrice().isEmpty()) {
try {
price = Integer.parseInt(row.getPrice());
} catch (NumberFormatException e) {
log.warn("해당 item 에 올바른 price 가 설정되어 있지 않습니다. {}: {}", row.getId(), row.getPrice());
}
}
return new Object[]{
row.getId(),
row.getItem(),
row.getBrand(),
price,
row.getDescription()
};
})
.toList();
...
jdbcTemplate.batchUpdate(insertSql, itemBatchArgs);
jdbcTemplate.batchUpdate(categorySql, categoryBatchArgs);
jdbcTemplate.batchUpdate(itemCategorySql, itemCategoryBatchArgs);
jdbcTemplate.batchUpdate(itemUrlSql, itemUrlBatchArgs);
jdbcTemplate.batchUpdate(itemJobSql, itemJobBatchArgs);
jdbcTemplate.batchUpdate(filterSql, filterBatchArgs);
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("CSV parsing 후 DB insert 하는 과정에서 Error", e);
throw new RuntimeException("CSV parsing 후 DB insert 하는 과정에서 Error", e);
}
}
2. JDBC Batch Insert 성능 확인

해당 test csv 파일의 데이터 100건으로 먼저 테스트해봤다.
- 2-1 기존 DataParser 의 JPA insert test 총 소요 시간

258210 milliseconds = 4분 18초
- 2-2 JDBC Batch Update insert 총 소요 시간

784 milliseconds = 0.784 초
99.7% 나 향상되는 유의미한 성능 차이가 있었다.
3. 분석 및 결론

JPA 에서 Transaction 을 commit 하게 되면 Entity Manager 는 우선 영속성 컨텍스트(Persistence Context) 를 flush 한다.
Flush 는 영속성 컨텍스트의 변경 내용을 DB 에 동기화하는 작업인데 이때 등록, 수정, 삭제한 entity 를 DB 에 반영한다.
(Flush는 변경된 내용을 DB에 즉시 반영해야 하기 때문에 많은 양의 데이터를 처리할 때 성능에 부하를 줄 수 있다.
하지만 hibernate.jdbc.batch_size 를 적절하게 설정해주면 flush 성능 부하 완화시켜줄 수 있다.)
이러한 부분은 JPA 내부적으로 이루어지기 때문에 사용하는 코드에서는 코드의 변경 없이 이러한 작업들이 가능하다.
그렇기 때문에 JPA 는 Transaction 을 관리하는데에 최적화가 되어있지만 단점으로는 위의 테스트와 같이 시간이 소요된다는 점이다.
JDBC 는 이러한 관리가 생략되고 단순히 데이터만 삽입해주기 때문에 유의미한 성능 차이가 났다고 생각한다.
JDBC Batch Insert 는 복잡하지 않은 연관관계 구조를 가지고 있다면 대용량 data insert 에 아주 적합한 것 같다.